Airbus (OTC: EADSY) space engineers have installed ESA’s European Robotic Arm (ERA) onto the Russian Multipurpose Laboratory Module (MLM) and it is now ready for its flight to the International Space Station (ISS). Together with this module, known as ‘Nauka’, ERA and its two control stations will launch from the Baikonur Cosmodrome, in Kazakhstan, on a Proton rocket.
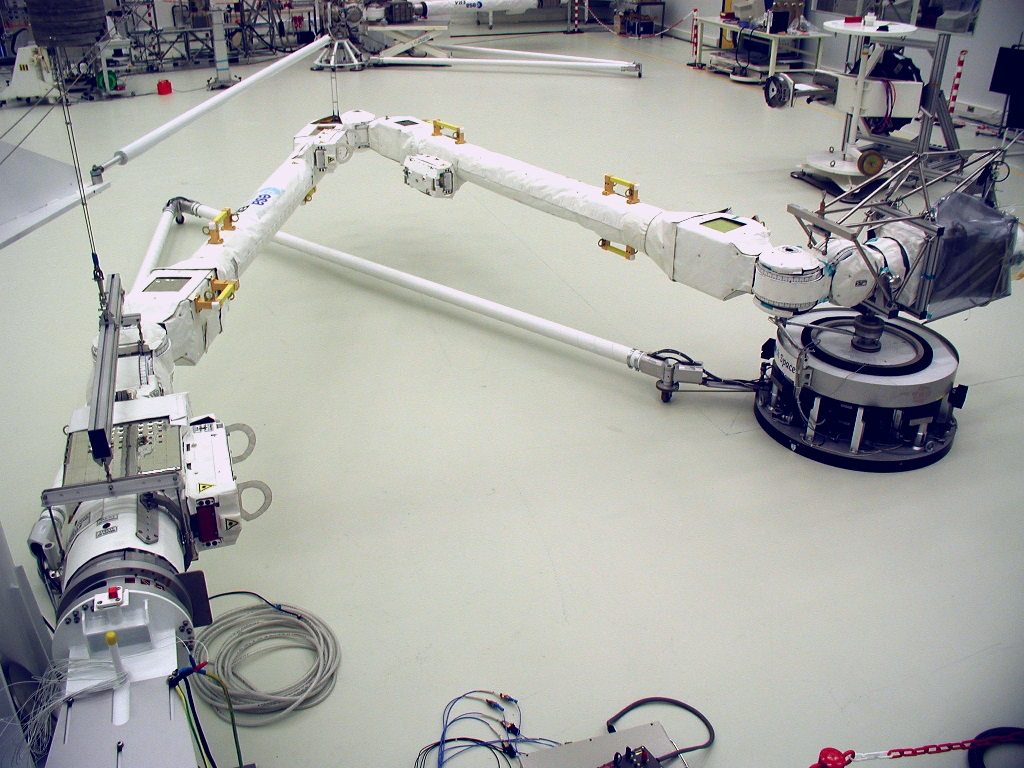
After a one-week journey the European Robotic Arm will arrive at the ISS, where it will service the Russian segment of the space station. With a total length of 11.3 metres, the symmetrical, two-handed intelligent robot arm can ‘walk’ around the exterior of the ISS, hand-over-hand from one fixed base-point to another. ERA’s seven robust and accurate joints, the lightweight limbs and the control computer in the middle of the arm give the robot arm its versatility.
Astronauts and cosmonauts can control the European Robotic Arm in real-time or pre-programme it from inside or outside of the ISS, to make it move payloads, inspect the space station with its infrared cameras and to support operations outside the ISS. From its tip, the robot provides electrical power, a data bus, a video line and a rotating drive machine. By connecting a tool to the tip, ERA can be equipped for one of the many tasks it can perform automatically or semi-automatically. ERA has a lightweight construction but thanks to the zero-gravity conditions in space, it can move very large masses: from 3,000 kg routinely up to 8,000 kg in slow modus. The robot arm operates with an accuracy of 5 millimetres.
ERA has been developed for European Space Agency (ESA) by a European consortium, led by Airbus Defence and Space in the Netherlands. Airbus designed the arm and its software functions, managed the development of subsystems throughout Europe and integrated and tested the system. In the last few months Airbus has integrated ERA on the MLM, together with ESA and Russian partners RSC/Energia.