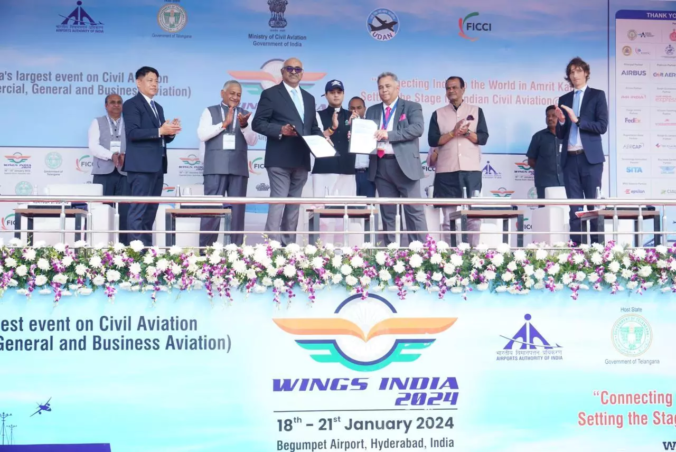
Hyderabad, Telangana, India, January, 2024 – Delivering on its commitment to ‘Skill India’, Airbus Group SE (Paris: AIR) has entered into a 50:50 joint venture with the Tata-owned Air India to launch a world-class pilot training centre in Gurugram, Haryana. The Tata Airbus Training Center will offer A320 and A350 flight training to some 5,000 new pilots over 10 years. The sprawling 3,300 sq.mt. centre will be equipped with 10 Full Flight Simulators (FFS), flight training classrooms and briefing and debriefing rooms as part of the complete Airbus Flight Training Device setup.
The training centre is due to be operational starting early 2025 with the initial installation of four A320 FFS. The Tata Airbus Training Centre will offer courses approved by Directorate General of Civil Aviation (DGCA) and European Union Aviation Safety Agency (EASA).
Airbus has also partnered with GMR Aero Technic to offer Aircraft Maintenance Engineering training courses at the latter’s facility in Hyderabad. Airbus will provide training material such as trainee handbooks, examination database, online access to Airbus customised training modules and Airbus Competence Training (ACT) for Academy media package. Airbus will also train GMR instructors and provide continual assessment of the training center.
Forward-Looking Statements
This press release may contains forward-looking statements within the meaning of the Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995, including expected delivery dates. Such statements are based on current expectations and projections about our future results, prospects and opportunities and are not guarantees of future performance. Such statements will not be updated unless required by law. Actual results and performance may differ materially from those expressed or forecasted in forward-looking statements due to a number of factors, including those discussed in our filings with the Securities and Exchange Commission.