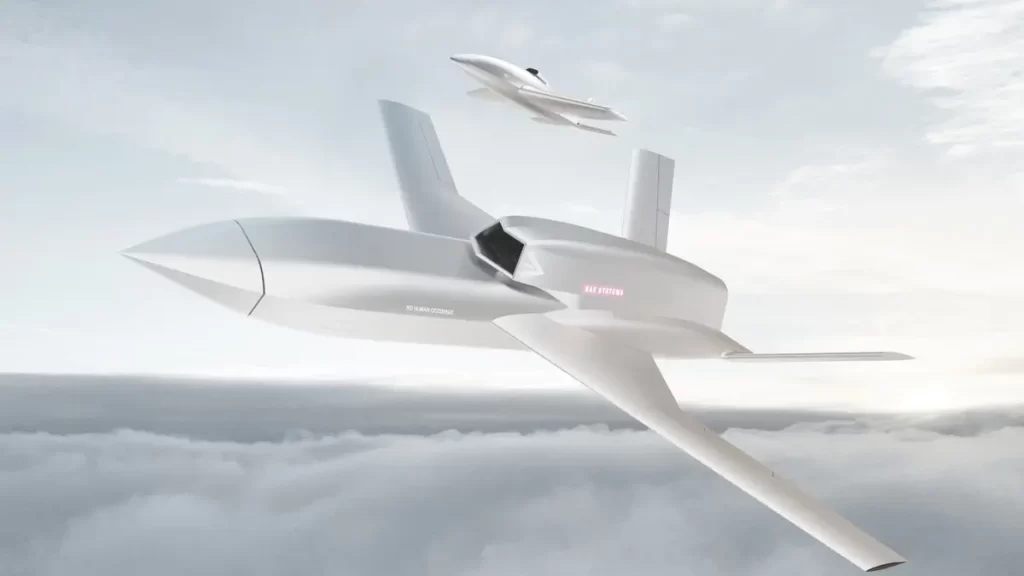
PHASA-35 completes first successful stratospheric flight
Over a 24-hour period, PHASA-35 soared to more than 66,000 feet, reaching the stratosphere, before landing successfully. The trial, completed last month in New Mexico in the USA, allowed engineers to assess the performance of…