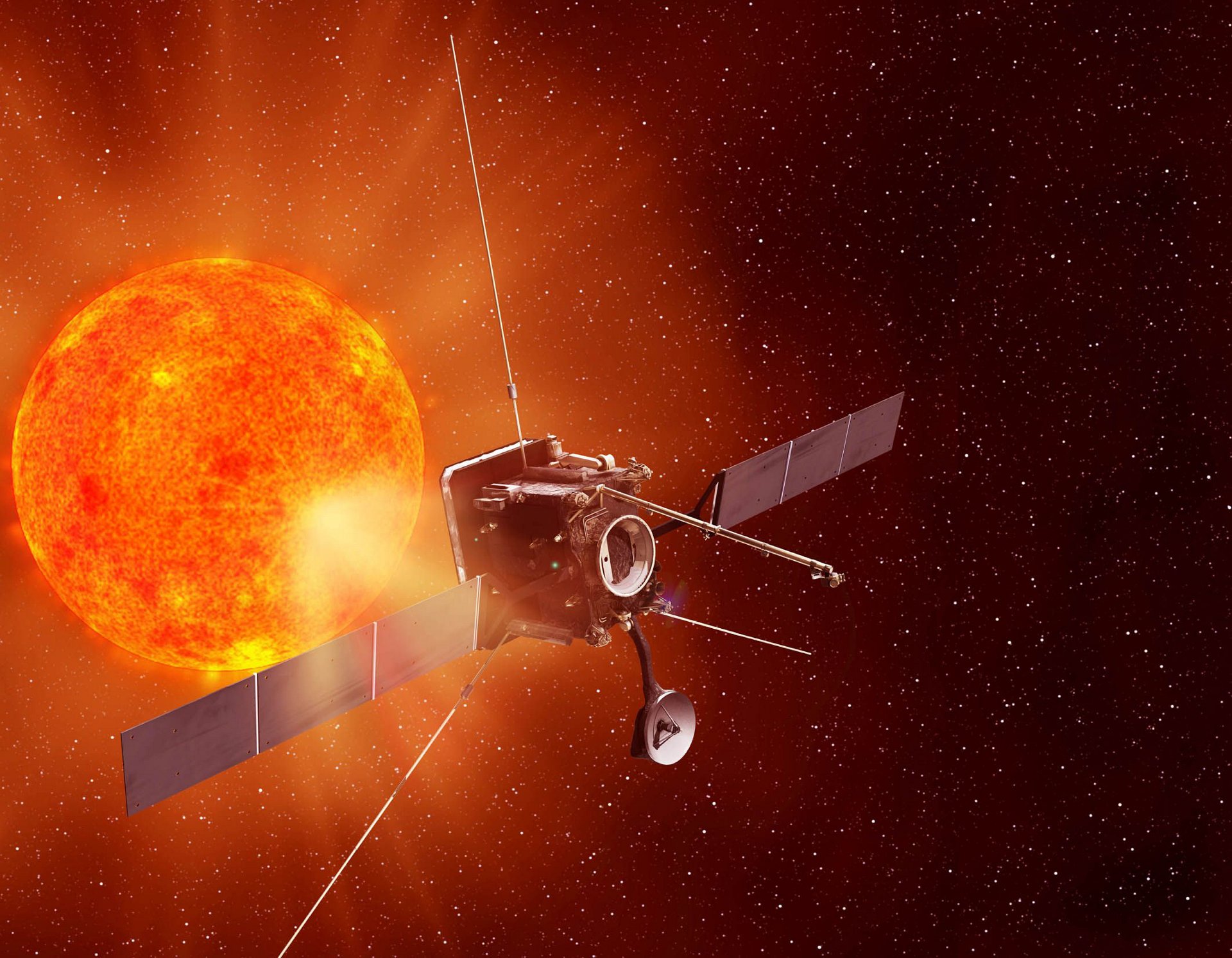
Currently traveling at some 105 million kilometres from Earth, the Airbus-built Solar Orbiter (SolO) is en route for an encounter to uncover the secrets of our closest star.
While humankind has been studying the Sun for hundreds of years, the research is limited because data was always collected from distances more or less equal to the star’s separation from Earth, according to Ian Walters, Airbus’ SolO Project Manager.
“Solar wind takes about two to four days to get from the Sun to Earth, and in that time, it transforms completely,” he explained. “We can better correlate what is seen with what is felt from the Sun if we can get up close. That’s the point of the Solar Orbiter mission…and it’s never been achieved before.”
Solar Orbiter was launched in February in a joint mission of the European Space Agency and the U.S. National Aeronautics and Space Administration. Travelling closer to the Sun than its nearest planet – Mercury – SolO will make comprehensive measurements of the nascent solar wind.

Beating the heat
For the spacecraft and its 10 instruments to survive extreme temperatures of up to 600 deg. Centigrade, Airbus designed a protective heat shield with openings for SolO’s five telescopes to peek through during the trek.
According to Walters, the most critical heat protection technology is the Stand-off Radiator Assembly (SORA) – a set of radiators sitting on the spacecraft’s side that is always in shadow, enabling them to quickly transfer heat from the instruments into space. SORA’s thermal straps are made from pyrolytic graphite, which is five times more conductive than copper wire but flexible like paper.
To avoid any molecular contamination that could compromise imagery from the telescopes, Airbus also built Solar Orbiter to levels of cleanliness far exceeding any other spacecraft built in the UK to date. Every item on SolO has been heated to over 120 degrees to make sure no gases are emitted in the vacuum of space.

Predicting solar events
Data from Solar Orbiter can help make significant improvements to everyday life, particularly when it comes to predicting solar flares and coronal mass ejections (CME) – the expulsions of plasma and its accompanying magnetic field from the sun, which can have a major impact on Earth.
“In 1859, one such episode took down the world’s telegraph network,” Walters said. “A similar event today would severely disrupt our power grids, mobile phone towers, navigation systems and many other critical technologies.”
He added: “If we could predict the CME was coming our way, we’d have about two days’ notice for emergency government committees to be activated and react, instead of the few minutes’ notice we receive today.”