RTX, Rafael plan new missile production facility in Camden, Arkansas
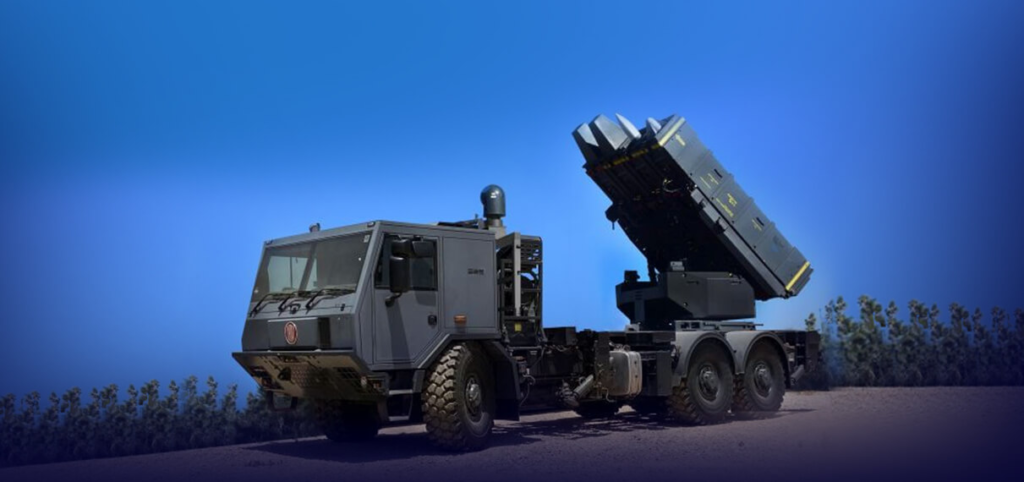
East Camden, Arkansas, October 26, 2023, PRNewswire - Raytheon, an RTX (NYSE: RTX) business, in partnership with Rafael Advanced Defense Systems, will build a manufacturing facility in East Camden, Arkansas to produce the Tamir missile…